In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, understanding how a business model works is crucial for entrepreneurs and companies seeking long-term success. A business model is not just about how a company makes money; it encompasses the entire strategy and approach to creating and delivering value to customers. This article will delve into the intricacies of business models and explore the various components and strategies that contribute to their effectiveness.
What is a Business Model? Why is it important?
A business model is a company’s profit-making plan that encompasses several key elements. It defines the products or services a company will offer, identifies its target market, and outlines the expected costs associated with the business operations. A business model is crucial for attracting investment, recruiting talent, and motivating staff while also playing a significant role in evaluating companies for investors and providing insights into a company’s future for employees. A successful business model should fulfill client needs at a competitive price and sustainable cost. Evaluating a business model involves analyzing factors such as gross profit, cash flow, pricing, and costs. There are various types of business models, including retailers, manufacturers, fee-for-service providers, and freemium providers.
A well-designed business model serves as the foundation for a company’s operations and growth. It outlines how the business creates, delivers, and captures value, reflecting management’s understanding of customer needs, market dynamics, and competitive advantage. A robust business model not only drives revenue generation but also guides decision-making and resource allocation, ultimately determining the company’s viability and longevity.
Creating Value for Customers
At the core of any successful business model is the ability to create value for customers. This value can take various forms, such as products, services, or shared assets. Understanding what customers want and need is essential for identifying opportunities and designing offerings that meet those requirements. By aligning value creation with customer preferences, businesses can establish a strong value proposition that sets them apart from competitors. Businesses must design their operations to ensure a seamless and positive customer experience, from the initial interaction to the final delivery of the product or service, ensuring a positive value delivery. Leveraging technology and digital tools can significantly enhance the delivery process, enabling businesses to reach a wider audience and streamline their operations.
Capturing value is the critical aspect of any business model. After creating and delivering value, businesses must find ways to monetize their offerings and generate revenue through various revenue streams, such as product sales, service fees, subscriptions, leases, or insurance premiums. It is essential to align pricing strategies with the perceived value by customers and ensure that the revenue generated outweighs the costs incurred in value creation and delivery.
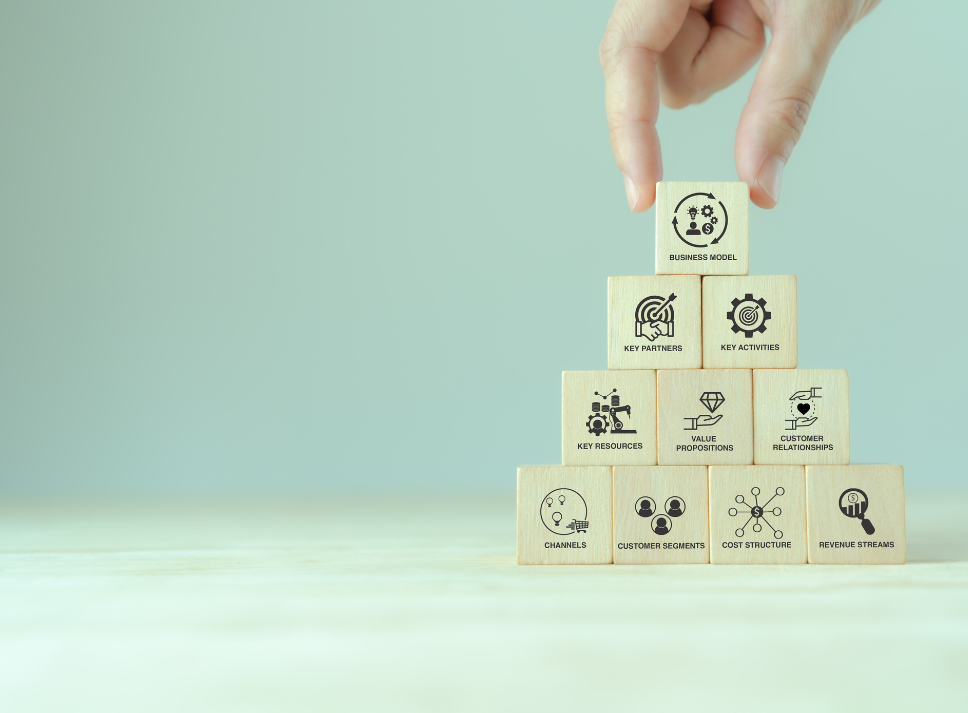
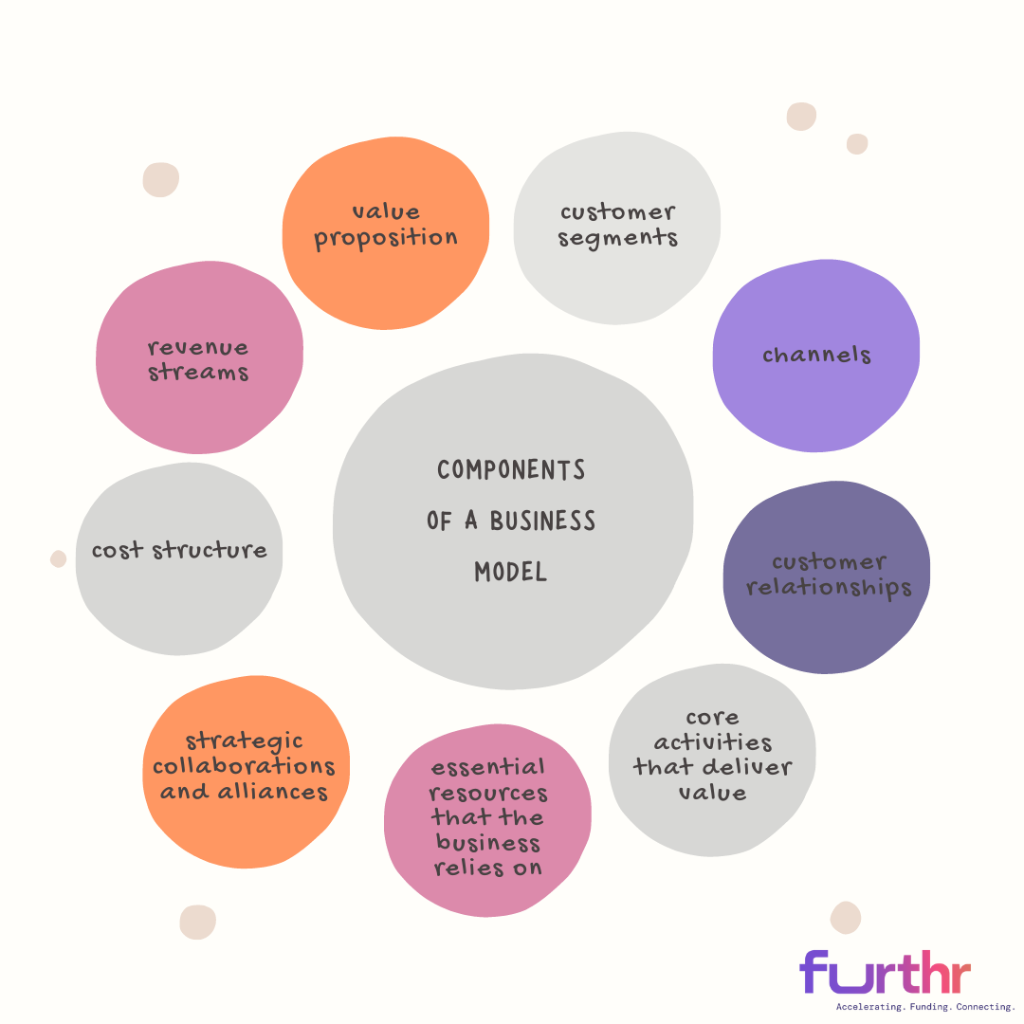
Components of a Business Model
The Business Model Process
Developing a robust business model involves a systematic and iterative process that aligns with the company’s goals and market dynamics. The following steps outline the typical business model process:
- Identify Customer Needs: Conduct market research and analysis to understand customer preferences, pain points, and unmet needs.
- Design Value Proposition: Develop a compelling value proposition that addresses customer needs and provides a unique selling point.
- Segment Customers: Divide the target market into distinct customer segments based on demographics, preferences, or behaviours.
- Select Channels: Determine the most effective distribution channels to reach and engage with customers.
- Build Customer Relationships: Establish strategies for building and nurturing strong relationships with customers, fostering loyalty and repeat business.
- Define Key Activities and Resources: Identify the core activities and resources required to deliver the value proposition effectively.
- Establish Key Partnerships: Identify potential partners or collaborators who can contribute to the business’s success and enhance its capabilities.
- Analyse Cost Structure: Assess the cost drivers and determine the most cost-effective ways to operate and deliver value.
- Design Revenue Streams: Develop revenue models and pricing strategies that align with the value delivered to customers.
- Test and Iterate: Continuously evaluate and refine the business model based on customer feedback, market changes, and emerging opportunities.
Developing a Business Model
When developing a business model, entrepreneurs and companies should consider several factors to ensure its effectiveness and sustainability. These factors include:
- Market Research: Gain a deep understanding of the target market, including customer needs, competitors, and industry trends.
- Innovation and Differentiation: Identify unique value propositions that set the business apart from competitors and address unmet market needs.
- Digital Transformation: Embrace digital technologies and leverage them to enhance operations, reach a broader audience, and deliver value more effectively.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Put the customer at the centre of the business model, focusing on delivering exceptional experiences and building long-term relationships.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Design the business model to accommodate growth and adapt to changing market conditions and customer preferences.
- Sustainability and Social Impact: Consider environmental and social factors in the business model, aligning with sustainable practices and addressing societal needs.
- Risk Management: Identify potential risks and uncertainties and develop strategies to mitigate them, ensuring the business model’s resilience.
Business Model Transformation
In today’s dynamic business environment, the ability to adapt and transform is crucial for long-term success. Business model transformation involves reimagining and reinventing the core elements of a business model to respond to market changes, technological advancements, or shifts in customer behaviour. This transformation could include:
- Digitalisation: Embracing digital technologies to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation.
- New Revenue Models: Exploring alternative revenue streams or pricing mechanisms to generate additional income.
- Ecosystem Partnerships: Collaborating with other businesses or stakeholders to create new value propositions and unlock synergies.
- Market Expansion: Expanding into new markets or target segments to diversify revenue sources and reach a broader customer base.
- Product or Service Innovation: Introducing new products or services that address emerging customer needs or leverage emerging technologies.
- Operational Efficiency: Optimising internal processes and resource allocation to improve productivity and reduce costs.
Business Model Analysis
Regular analysis and evaluation of the business model are essential to ensure its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. Business model analysis involves:
- Performance Metrics: Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the business model’s success, such as revenue growth, customer retention, or market share.
- Customer Feedback: Soliciting feedback from customers to assess their satisfaction, identify pain points, and uncover opportunities for improvement.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Comparing the business model to competitors to identify strengths, weaknesses, and potential areas of differentiation.
- Market Trends: Monitoring industry trends and market dynamics to identify emerging opportunities or threats that may impact the business model.
- Risk Assessment: Conducting a comprehensive assessment of potential risks and vulnerabilities that may affect the business model’s viability.

Types of Business Models
There are various types of business models, each suited to different industries, markets, and customer segments. Some common business models include:
- Product-Based: Focuses on creating and selling physical or digital products to customers.
- Service-Based: Centers around providing services or expertise to customers, often on a consulting or subscription basis.
- Platform-Based: Facilitates interactions between users or businesses through a digital platform, generating revenue from transactions or advertising.
- Subscription-Based: Offers customers access to products or services for a recurring fee, ensuring regular and predictable revenue.
- Freemium: Provides a basic version of a product or service for free, with premium features available for a fee.
- E-commerce: Enables online buying and selling of products, often leveraging technology and digital platforms.
- Franchise: Involves granting individuals or businesses the right to operate under an established brand and business model in exchange for fees or royalties.
- Sharing Economy: Connects individuals or businesses to share resources or services, often through digital platforms.
Choosing the Right Business Model
Selecting the right business model depends on various factors, including the nature of the industry, customer preferences, competitive landscape, and the company’s capabilities. Businesses should consider the following when choosing a business model:
- Market Analysis: Understand the target market, customer needs, and industry dynamics to identify the most viable business model.
- Competitive Advantage: Assess the company’s unique strengths and differentiators to determine which business model aligns best with its capabilities.
- Customer Research: Conduct surveys, interviews, or market research to gain insights into customer preferences, pain points, and willingness to pay.
- Revenue Potential: Evaluate the revenue-generating potential of different business models, considering factors such as pricing, scalability, and market demand.
- Resource Requirements: Assess the resources, skills, and infrastructure needed to execute the chosen business model effectively.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Choose a business model that allows for future growth, innovation, and adaptation to changing market conditions.
Advantages of a Strong Business Model
A well-designed business model offers several advantages for companies, including:
- Competitive Advantage: A unique and effective business model sets the company apart from competitors and enables it to capture market share.
- Value Creation: By focusing on creating and delivering value to customers, businesses can establish strong customer loyalty and generate repeat business.
- Scalability: A scalable business model allows for growth and expansion without significant increases in costs or resource requirements.
- Adaptability: A flexible business model can adapt to changing market conditions, technological advancements, or customer preferences.
- Resilience: A robust business model can withstand economic downturns, industry disruptions, and other external challenges, ensuring long-term sustainability.
The Significance of Business Models in Post-Pandemic era
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a disproportionate impact on businesses worldwide, causing significant disruptions across industries. However, it has also presented opportunities for innovation, digital transformation, and the development of more sustainable business models. In Ireland, for example, SMEs have faced both challenges and opportunities, with some experiencing positive impacts or finding ways to sustain their operations amidst the uncertainty. The pandemic has underscored the importance of digital capabilities, customer-centricity, and transformation readiness in navigating crises and driving long-term value.
As businesses reimagine their operations and strategies in the post-pandemic era, business model adaptation and transformation have become crucial. The acceleration of digitisation initiatives, the exploration of new revenue models, and a focus on sustainability and social impact are key trends observed among Irish SMEs. Furthermore, talent attraction and retention, along with strategic partnerships, are vital considerations for SMEs seeking to thrive in the evolving business landscape.
Conclusion
Understanding how a business model works is essential for entrepreneurs and companies striving for success in today’s dynamic and competitive business environment. A well-designed business model enables value creation, efficient delivery, and effective revenue generation. By considering market dynamics, customer needs, and industry trends, businesses can develop robust and adaptable business models that drive growth, innovation, and long-term sustainability. As the post-pandemic era unfolds, businesses must embrace transformation and leverage their business models to navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and deliver value to customers and stakeholders.



